Extra! Extra! Read All About It! Total Lunar Eclipse 7 September 2025
This is a celestial event you won’t want to miss — and one of the best lunar eclipses visible from South Africa in years.
Stargazers around the country have been waiting impatiently for a stunning astronomical spectacle that’s taking place on the night of Sunday the 7th of September 2025, when a rare total lunar eclipse, commonly called a Blood Moon, will be visible across the country. Grab your warm jackets (it can still be cold during September evenings) and get comfortable as the sky puts on an amazing show!
Vox Weather Meteorologist Michelle du Plessis tells us more about how lunar eclipses are formed, and the weather we can hope for on Sunday night.
What is a Lunar Eclipse?
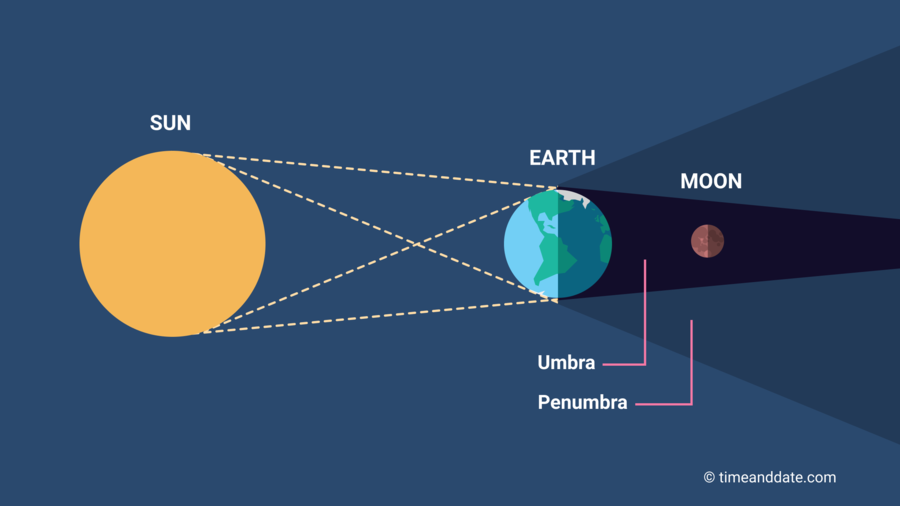
A lunar eclipse happens when the Earth passes directly between the Sun and the Moon, casting its shadow onto the Moon. This only occurs during a full moon.
There are three types of lunar eclipses:
- Penumbral Lunar Eclipse – the Moon passes through Earth’s faint outer shadow (the penumbra), causing only a slight dimming.
- Partial Lunar Eclipse – part of the Moon passes through Earth’s dark central shadow (the umbra), and a section appears darkened.
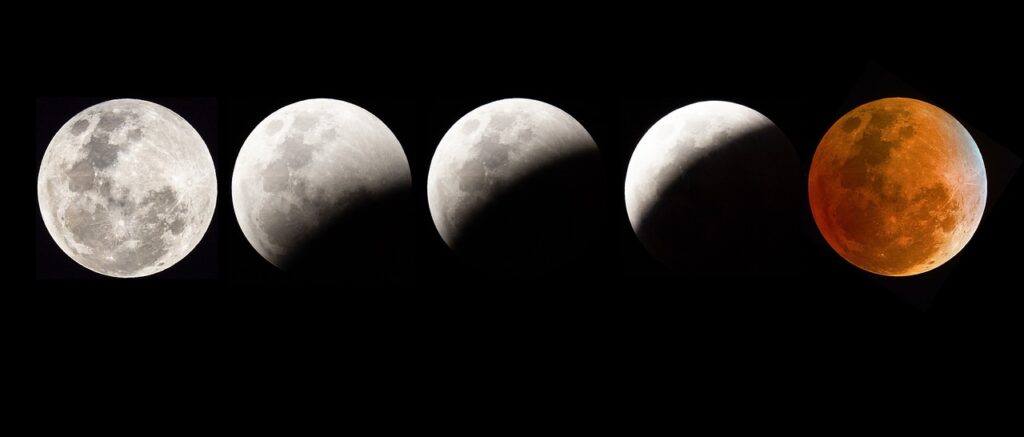
- Total Lunar Eclipse – the entire Moon moves into Earth’s umbra, turning a reddish colour — often called a ‘Blood Moon’.
During a total lunar eclipse, the Earth blocks direct sunlight from reaching the Moon. However, sunlight still filters through Earth’s atmosphere and bends (or refracts) around the planet.
Shorter blue wavelengths are scattered, and the longer red and orange wavelengths reach the Moon — causing it to glow red or copper.
It’s the same effect that gives us red sunrises and sunsets — except this time, you’re seeing it reflected back from the Moon!
This TikTok video from Michelle shows us more on how lunar eclipses take place – together with a quick weather overview for the country’s stargazing.
The 7 September 2025 eclipse is special because:
- It will be a total lunar eclipse, with the entire Moon turning red.
- It will last 82 minutes, making it one of the longest lunar eclipses of the decade.
- It will be visible across South Africa.
- No telescope is needed — you can see it with the naked eye if skies are clear.

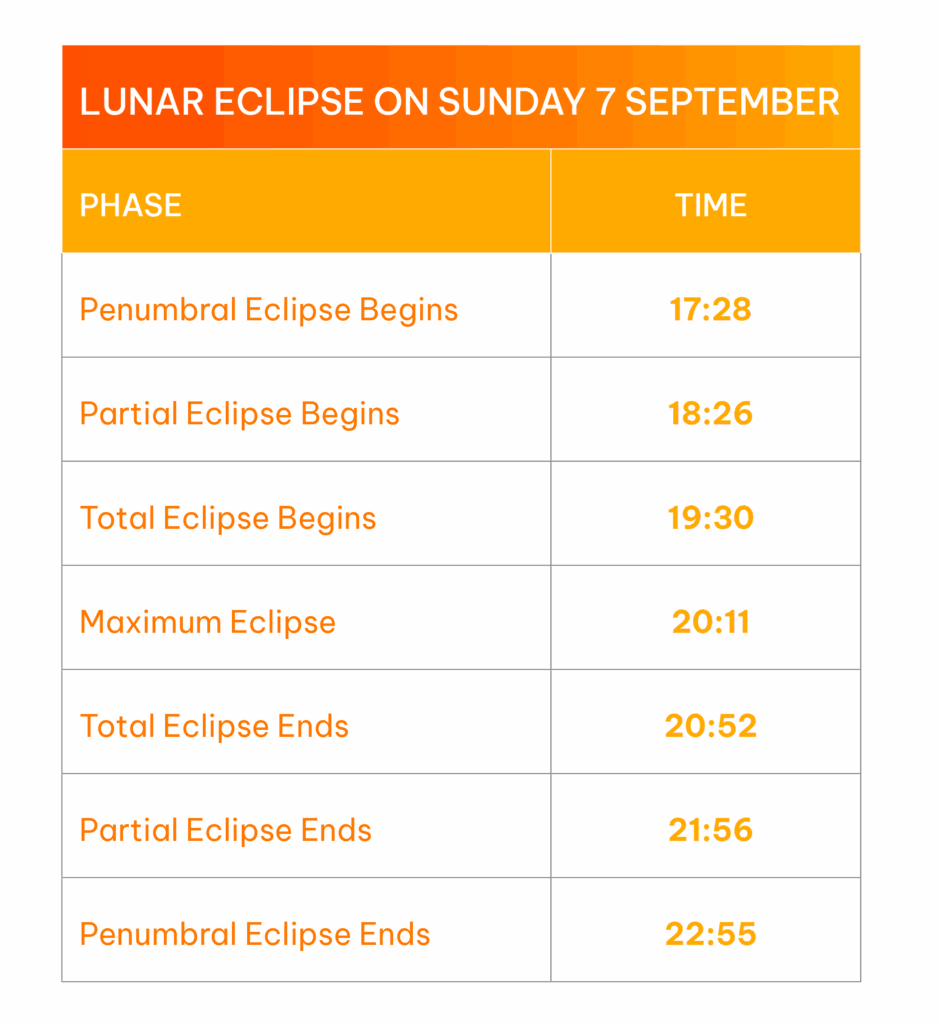
South Africa Viewing Details and Weather Conditions
The table shows the key moments to look out for. The best time to watch is between 7:30 PM and 8:52 PM, when the Moon will be completely within Earth’s shadow and glowing red.
The weather conditions for 7 September across the country will be mostly favourable for viewing the total lunar eclipse on Sunday evening.
- However, around the Southern Cape, including parts of the Garden Route and Overberg, we are expecting widespread cloud cover, which will most likely obscure the view of the eclipse.
- In contrast, much of the interior, including the Free State, North West, Limpopo, and Gauteng, will experience partly cloudy skies with high to mid-level cloud, allowing for intermittent but generally good visibility of the eclipse.
- Cape Town is also expected to have clear enough skies, especially earlier in the evening, making for a great viewing opportunity.
- Coastal areas in KwaZulu-Natal and parts of the Eastern Cape may see some coastal cloud or mist, especially early evening, but breaks in the cloud are possible later on.
For the best view, try to find an open area away from city lights — ideally elevated, with an unobstructed view of the eastern horizon where the Moon will rise.
Tips for Watching and Photographing
- Dress warmly — it’s still chilly at night in September.
- Use a camera with manual exposure settings if possible.
- For smartphone users: Tap to focus on the Moon and reduce brightness for better contrast.
Fun Facts
- A lunar eclipse can only occur during a full moon.
- Unlike a solar eclipse, lunar eclipses are safe to view with the naked eye.
- The Moon doesn’t completely disappear — it turns red due to Rayleigh scattering in Earth’s atmosphere.
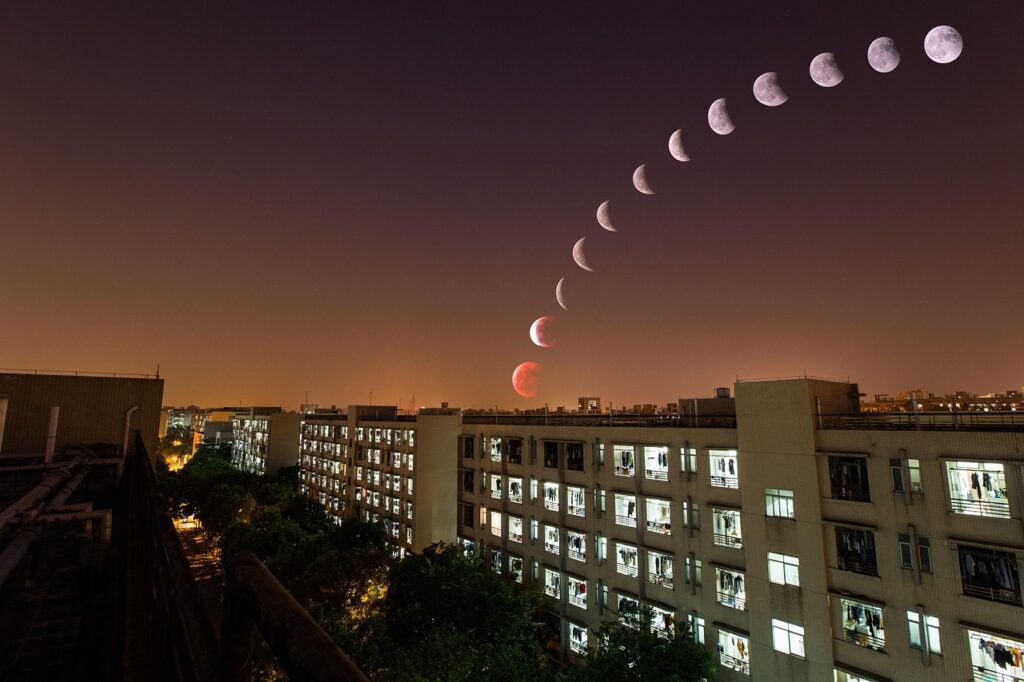

Why Is It Called a “Blood Moon”?
The term ‘Blood Moon’ comes from the deep red colour the Moon takes on during totality. Ancient cultures often saw it as an omen, but today we know it’s simply the effect of Earth’s atmosphere bending sunlight.
Mark your calendars and if skies are clear, look up and enjoy the show!

